Refrigerated units for scientific applications
-
General characteristics
The pharmaceuticals and health services sectors are growing in terms of social-economic importance, becoming strategic, as highlighted by the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the scientific field, there are various applications with specific needs depending considerably on the nature of the stored materials.
Indeed, attention to the storage quality of the contents of refrigerated units is central when carrying out technical-economic assessments, as stored substances can often be of very high economic or strategic value.In scientific applications, units can be categorised according to the product being stored.
Blood, plasma, blood derivatives
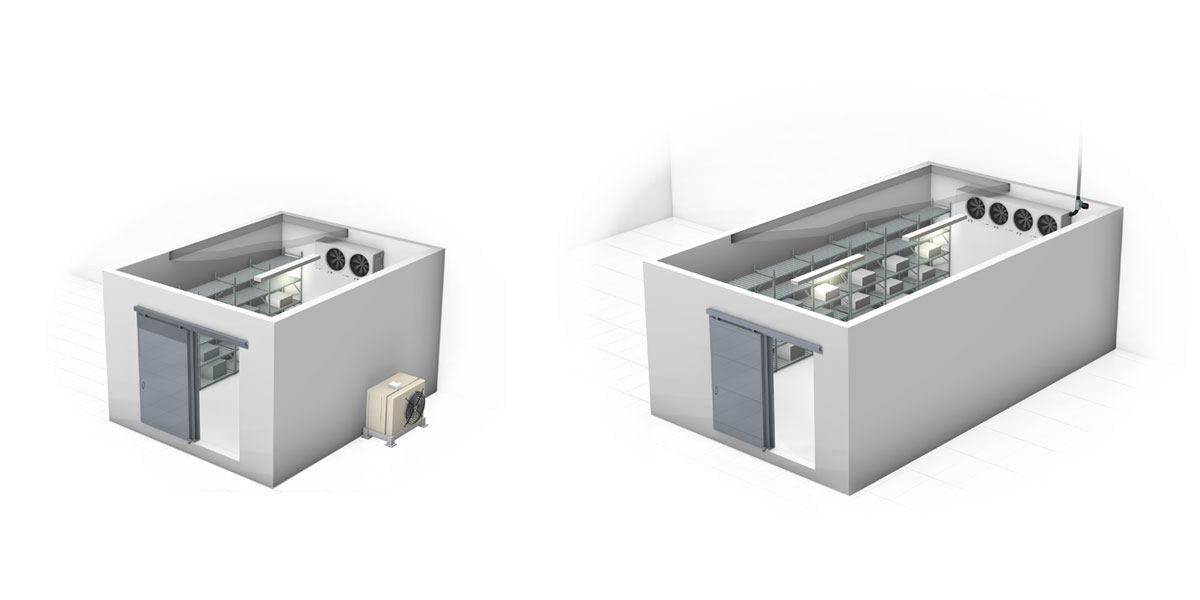
These refrigerators store different types of biomedical supplies (blood derivatives, blood, plasma, etc.) at a controlled temperature.
For safety reasons, in addition to the refrigerator, the system also needs to include monitoring equipment for controlling, signalling and recording temperatures at regular intervals. Again for safety reasons, lockable doors may be required to protect access to the contents and ensure the unit remains sealed.
Appliances storing blood derivatives may require specialist refrigeration units to ensure compliance with legal requirements and maintain high standards for the safety of patients who will receive the contents.
Hardware and software redundancy with a backup function may be required to satisfy the requirements of maximum reliability.
These units are typically installed in hospitals or blood banks, however may also be used in laboratories for the storage of materials classified as high risk.Medicines and vaccines
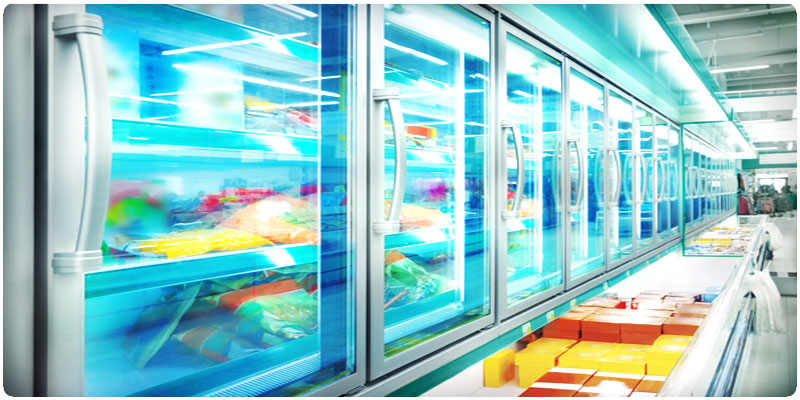
Professional refrigerators for pharmaceuticals and medicines, with one or two temperatures, designed specifically to guarantee the correct storage conditions for healthcare products, thermosensitive biological materials and all types of drugs, in accordance with the indications of the pharmaceutical companies.
Their surfaces must be designed for easy and complete disinfection and the units must be highly reliable, in particular as regards maintaining the required temperature.
These types of units are typically installed in pharmacies, health & beauty stores, and hospitals for the storage of low-risk materials.Samples for analysis and reagents
Laboratory refrigerators are mainly used for the storage of samples (biological and non-biological) and reagents, and maintain a constant temperature to minimise the risk of cross-contamination or explosion of volatile materials. To maintain a stable and uniform temperature, they are typically equipped with a fan to circulate the air inside the unit and avoid stratification; to prevent the release of cold air from the unit, the fan switches off automatically when the door is opened.
To avoid cross-contamination, laboratory refrigerators often have several separate compartments to ensure that the different types of stored materials never come into contact with each other.
These units are typically found in scientific laboratories. -
Plus
Scientific applications require maximum reliability in preserving the contents in the specified conditions. It is crucial to report all situations in which the temperature exits the limits of compliance, so as to have full control of any out-of-range situations.
The main benefits of CAREL’s solutions for scientific applications include:- Automatic recording of temperature data for long periods of time
- Battery backup for recording temperatures even during blackouts
- Quick and easy identification of the type of alarm: on the front of the unit and from the centralised system
- Specific alarms
- Rapid response times in the event of alarms
- Flexibility to upgrade from low to high risk applications with data loggers on existing or new units
- Purchase bundles including units and maintenance plan.